Introduction
Blockchain technology has emerged as a transformative innovation across various industries, revolutionizing the way transactions are recorded, verified, and stored. Initially conceptualized as the underlying technology for Bitcoin, blockchain has since found applications beyond cryptocurrencies, extending to finance, supply chain management, healthcare, and government operations. This article explores the benefits and challenges of blockchain technology, highlighting its potential impact and the obstacles that must be overcome for wider adoption.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger system that records transactions across multiple nodes securely and transparently. Unlike traditional databases, blockchain operates without a central authority, ensuring data integrity and reducing the risk of fraud and tampering. Each block in the chain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, timestamped transaction data, and a unique identifier, making it highly resistant to alterations.
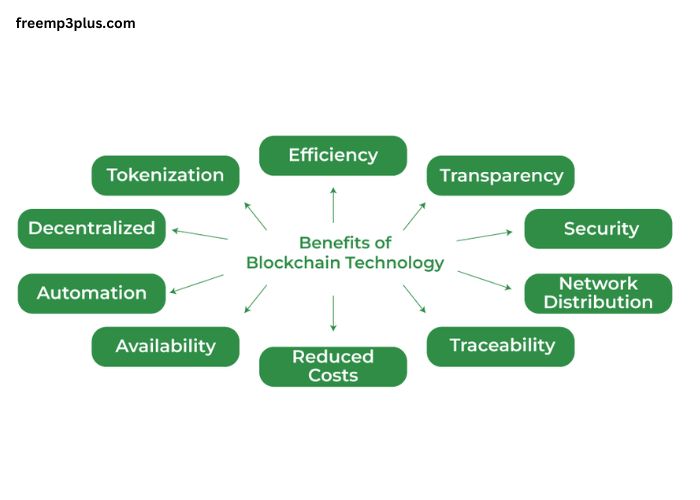
Benefits of Blockchain Technology
1. Enhanced Security
One of the primary advantages of blockchain technology is its robust security framework. Transactions are encrypted using advanced cryptographic techniques, making them nearly impossible to alter or delete. Additionally, blockchain operates on a decentralized network, eliminating the risk of single-point failures and cyberattacks.
2. Transparency and Trust
Blockchain provides a transparent and immutable ledger of transactions accessible to all participants within the network. This transparency fosters trust among stakeholders, reducing the need for intermediaries in various industries such as banking, supply chain, and legal services.
3. Decentralization
Unlike traditional centralized systems controlled by a single entity, blockchain operates on a decentralized network. This decentralization reduces dependency on intermediaries, minimizes operational costs, and enhances the overall reliability of the system.
4. Cost Efficiency
Blockchain technology eliminates the need for third-party verification, significantly reducing transaction fees. In industries such as cross-border payments, this reduction in costs can lead to substantial savings for businesses and consumers alike.
5. Faster Transactions
Traditional financial transactions often require intermediaries, leading to delays in processing. Blockchain technology streamlines transactions by enabling peer-to-peer interactions, reducing processing times from days to minutes.
6. Improved Traceability
Industries such as supply chain management benefit greatly from blockchain’s traceability features. With blockchain, every step of a product’s journey is recorded and verified, enhancing accountability and reducing fraud and counterfeit issues.
7. Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with predefined conditions stored on the blockchain. These contracts automate processes, reducing paperwork, minimizing disputes, and ensuring compliance without the need for intermediaries.
8. Data Integrity and Immutability
Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This immutability ensures data integrity, making blockchain an ideal solution for applications requiring secure and tamper-proof records, such as voting systems and legal documentation.
9. Financial Inclusion
Blockchain has the potential to provide financial services to unbanked populations, allowing them to access banking, lending, and investment opportunities without requiring traditional financial institutions.
10. Tokenization of Assets
Blockchain enables the tokenization of real-world assets such as real estate, stocks, and commodities. This innovation enhances liquidity, facilitates fractional ownership, and simplifies asset transfers.
Challenges of Blockchain Technology
1. Scalability Issues
One of the major challenges facing blockchain technology is scalability. As the number of transactions increases, the network may experience congestion, leading to slower transaction speeds and higher fees. Solutions such as sharding, layer 2 protocols, and off-chain transactions are being explored to address this issue.
2. Energy Consumption
Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanisms, used by Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, require significant computational power, leading to high energy consumption. This environmental impact has raised concerns about the sustainability of blockchain technology. Alternatives like Proof-of-Stake (PoS) and hybrid models are being developed to mitigate energy consumption.
3. Regulatory Uncertainty
Blockchain operates in a rapidly evolving regulatory landscape. Governments and regulatory bodies are still formulating policies regarding blockchain applications, creating uncertainty for businesses and investors. Compliance with existing financial and data protection regulations remains a challenge for widespread adoption.
4. Integration with Existing Systems
Many businesses rely on traditional IT infrastructures that may not be compatible with blockchain technology. Integrating blockchain into existing systems requires significant investment, time, and technical expertise.
5. Privacy Concerns
While blockchain ensures transparency, it also raises privacy concerns, particularly in industries dealing with sensitive data such as healthcare and finance. Solutions such as zero-knowledge proofs and private blockchains are being explored to enhance privacy while maintaining transparency.
6. Legal and Contractual Challenges
Smart contracts operate based on pre-defined conditions, but legal frameworks governing these contracts are still in development. Issues related to contract enforcement, dispute resolution, and jurisdiction pose challenges for businesses adopting blockchain-based solutions.
7. Security Risks and Vulnerabilities
While blockchain itself is secure, vulnerabilities can arise from poorly coded smart contracts, private key mismanagement, and potential 51% attacks in Proof-of-Work networks. Implementing robust security measures and auditing protocols is essential to mitigate these risks.
8. High Initial Costs
Implementing blockchain technology requires significant investment in infrastructure, research, and development. Businesses must evaluate the cost-benefit ratio before adopting blockchain solutions.
9. Limited Adoption and Awareness
Despite its potential, blockchain adoption remains limited due to a lack of awareness and understanding among businesses and consumers. Education and awareness campaigns are crucial for promoting blockchain technology and its benefits.
10. Governance Challenges
Decentralized networks often face governance challenges in decision-making and protocol upgrades. Achieving consensus among network participants can be complex, leading to forks and disagreements within the community.
Future of Blockchain Technology
The future of blockchain technology looks promising, with continuous advancements addressing its current challenges. Innovations such as layer 2 scaling solutions, cross-chain interoperability, and decentralized finance (DeFi) are driving blockchain’s evolution. Governments and enterprises are exploring blockchain applications in digital identity, voting systems, and transparent governance.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with blockchain is also gaining traction, enhancing data analysis, automation, and security. Additionally, the rise of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and the metaverse showcases blockchain’s potential in digital ownership and content monetization.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology offers numerous benefits, including enhanced security, transparency, cost efficiency, and decentralization. However, challenges such as scalability, regulatory uncertainty, and energy consumption must be addressed for broader adoption. As technology evolves and innovative solutions emerge, blockchain is poised to reshape industries and revolutionize digital interactions in the coming years. Businesses and policymakers must collaborate to create an environment that fosters blockchain innovation while addressing its limitations.